Factorial is a mathematical operator. If we take factorial of 5 then its equal to 5x4x3x2x1. Factorial is represented by ! or ㄴ. If n is the number then factorial of n can be represented by n! or ।n.
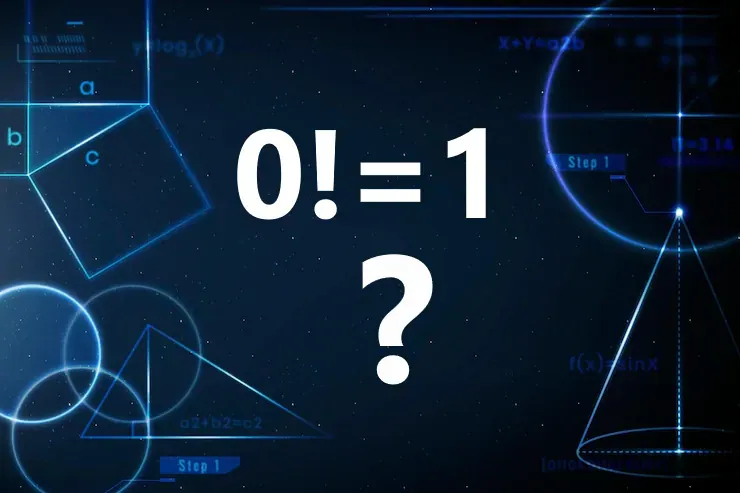 |
| Why factorial of zero is equals to one not zero - 0! = 1 ? |
For example:
2! = 2x1
3! = 3x2x1
4! = 4x3x2x1
5! = 5x4x3x2x1
n! = nx(n-1)x(n-2)x(n-3)x.............
From above now we have a basic idea about factorial. We have a got a chapter called Permutation and Combination in class 10, 11 and 12 mathematics or advance mathematics.
From that chapter we know, When r ≤ n then
nPr=n!
/
(n-r)!⇒Now when r = 1
⇒nP1=n!
/
(n-1)!
⇒nP1=n(n-1)! / (n-1)!
⇒nP1=n
⇒nP1=n(n-1)! / (n-1)!
⇒nP1=n
⇒Now when r = 2
⇒nP2=n!
/
(n-2)!
⇒nP2=n(n-1)(n-2)! / (n-2)!
⇒nP2=nx(n-1)
⇒nP2=n(n-1)(n-2)! / (n-2)!
⇒nP2=nx(n-1)
⇒Now when r = 3
⇒nP3=n!
/
(n-3)!
⇒nP3=n(n-1)(n-2)(n-3)! / (n-3)!
⇒nP3=nx(n-1)x(n-2)
⇒nP3=n(n-1)(n-2)(n-3)! / (n-3)!
⇒nP3=nx(n-1)x(n-2)
From above we can conclude that
nP1=n
nP2=nx(n-1)
nP3=nx(n-1)x(n-2)
nP2=nx(n-1)
nP3=nx(n-1)x(n-2)
nPn=nx(n-1)x(n-2)x(n-3)x........=n!
nPn=n!
⇒n!
/
(n-r)!=n!
⇒n! / (n-n)!=n!
⇒n! / 0!=n!
⇒0!=n! / n!
⇒0!=1
That is why factorial of zero is equal to one note zero i.e. 0! = 1 is true.
Tags:
Mathematics